/blog
Blog Posts
- all
- blockchain
- technology
- governance
- contract
- dao
- bitcoin
- autonomous
- eos

What is the Legal Standing of a DAO?
This post explores the legal standing of DAOs and provides insight on how to structure your DAO to minimize liability for its members. A DAO, aka Decentralized Autonomous Organization, leverages blockchain technology to empower a group of people to reach a consensus over the state of their organization. I originally coined the phrase “Decentralized Autonomous Company” in 2013 to describe Bitcoin. The thinking was that Bitcoin was autonomously achieving its purpose without reliance on any centralized infrastructure.
What is Fractal Democracy?
Fractal Democracy enables a group of people to govern themselves without being captured by hidden, non-democratic, power structures. It does not make any ideological claims. Winston Churchill once said that “democracy is the worst form of government - except for all the others that have been tried”, but what if there are a multitude of ways to measure the will of the people, and some work while others fail miserably? Fractal Democracy is the best approach to tapping the wisdom of the crowds and reaching consensus on everything from leaders to budgets to laws.

Fractally — The Next Generation of DAOs
It’s time to introduce next generation of decentralized autonomous organizations.
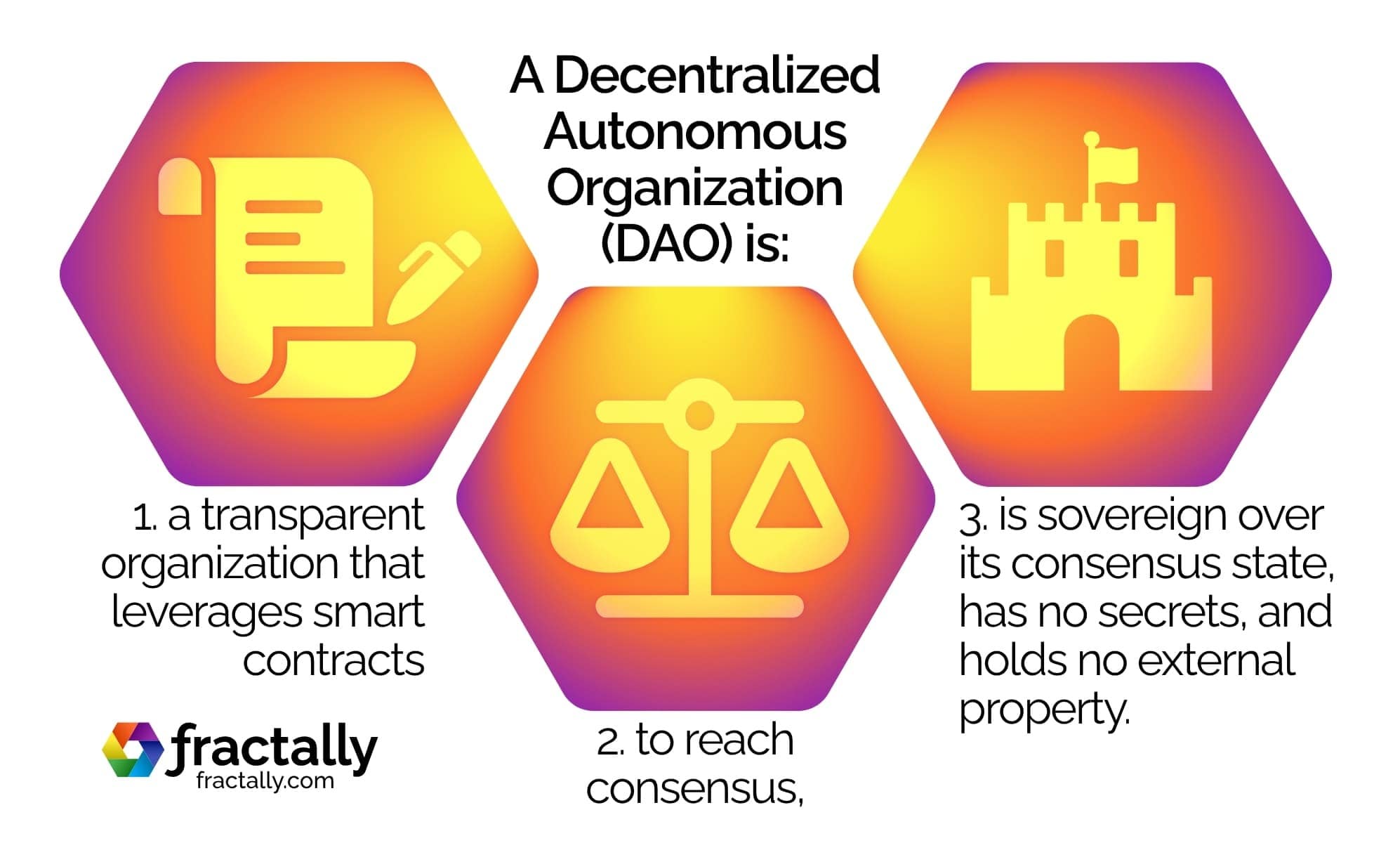
What is a DAO?
DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. The description “decentralized and autonomous” was originally coined by ƒractally’s founder, Daniel Larimer, in 2013, to describe the economics of Bitcoin. Larimer described Bitcoins as “shares” in a decentralized company which issued shares in exchange for hashpower.
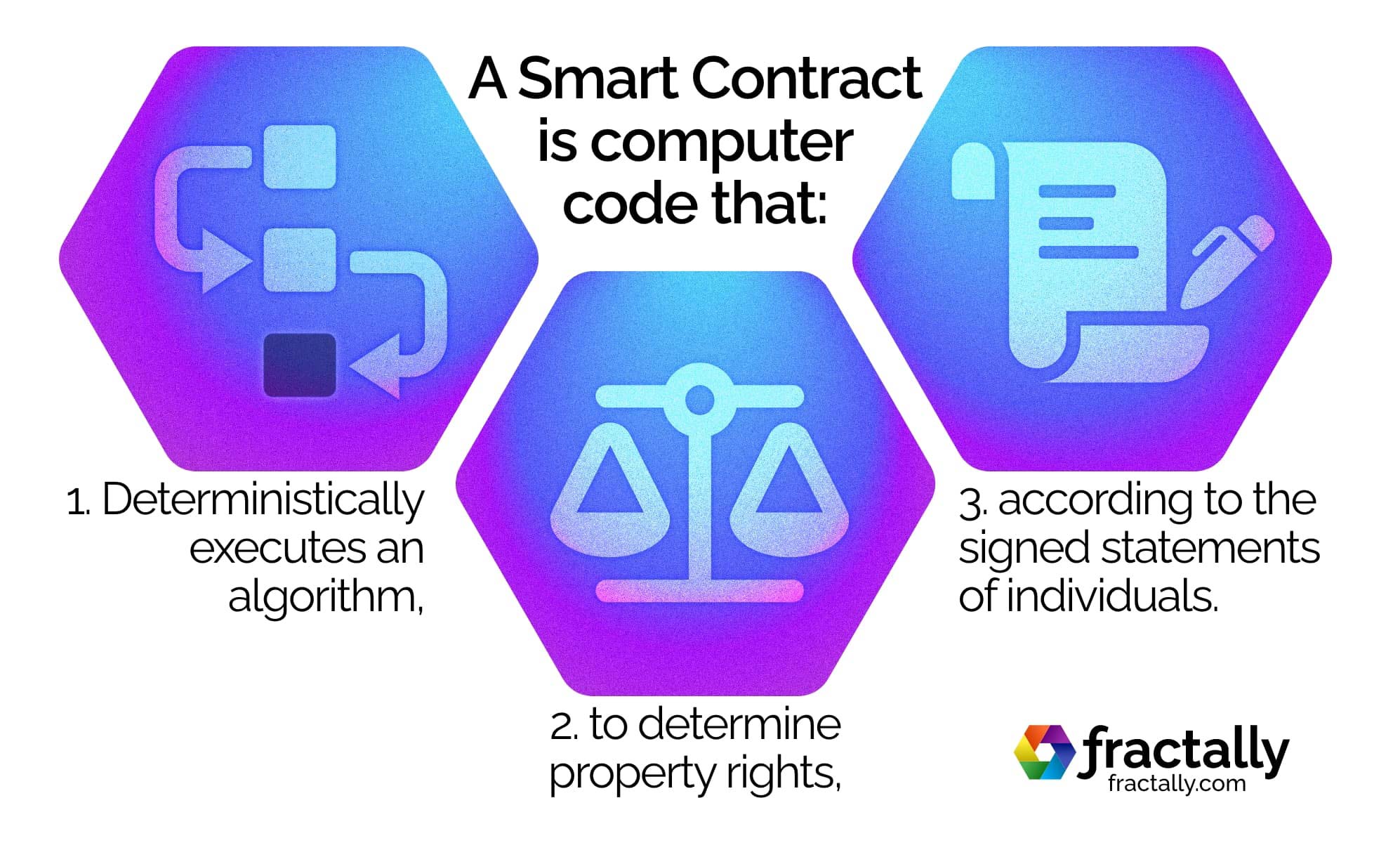
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is computer code that deterministically executes an algorithm to determine property rights according to the signed statements of individuals. They enable a community to efficiently and unambiguously reach a shared consensus on who owns what.
